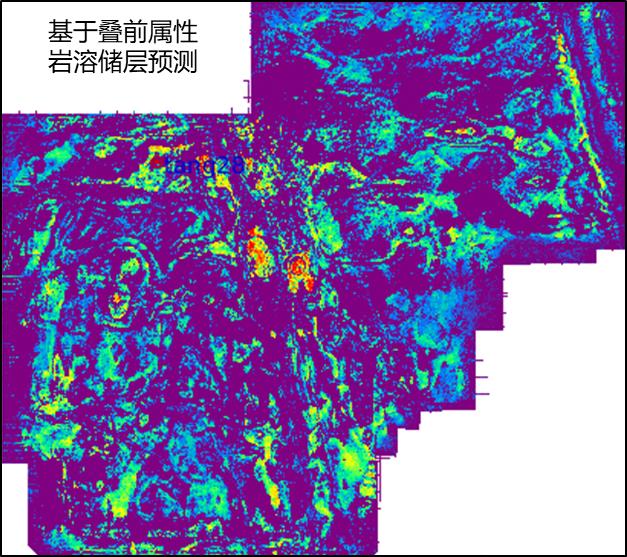
Research on key technology and method of karst fracture-cave reservoir prediction of Maokou Formation in Sichuan Basin
The project is commissioned by Sinopec Exploration Branch. Its purpose is to make use of the drilling results of Well He-30, 004-1, Tang-28 in adjacent areas, combine with newly acquired 3D seismic data in Lizi area to carry out the research on technical methods for predicting karst fracture and cave reservoir of Maokou Formation, to clarify exploration potential and objectives of the karst fracture and cave reservoir of Maokou Formation and lay a foundation for exploration deployment in this area.
Through research of this project, aiming at the characteristics of thin karst fracture-cavity reservoir and inconspicuous characteristics, a systematic, pre-stack and post-stack combination of karst fracture-cavity reservoir prediction key technologies, technical flow have been formed. As shown in the figure below, it includes one important basic processing: pre-stack gathers optimization processing; 4 key technical links: paleogeomorphology, micro-paleogeomorphology analysis, karst prediction based on paleogeomorphology, post-stack karst and pre-stack karst prediction; 3 supporting technologies: pre-stack gradient DSER similarity volume, morphological structure analysis, and model trace difference prediction technology.
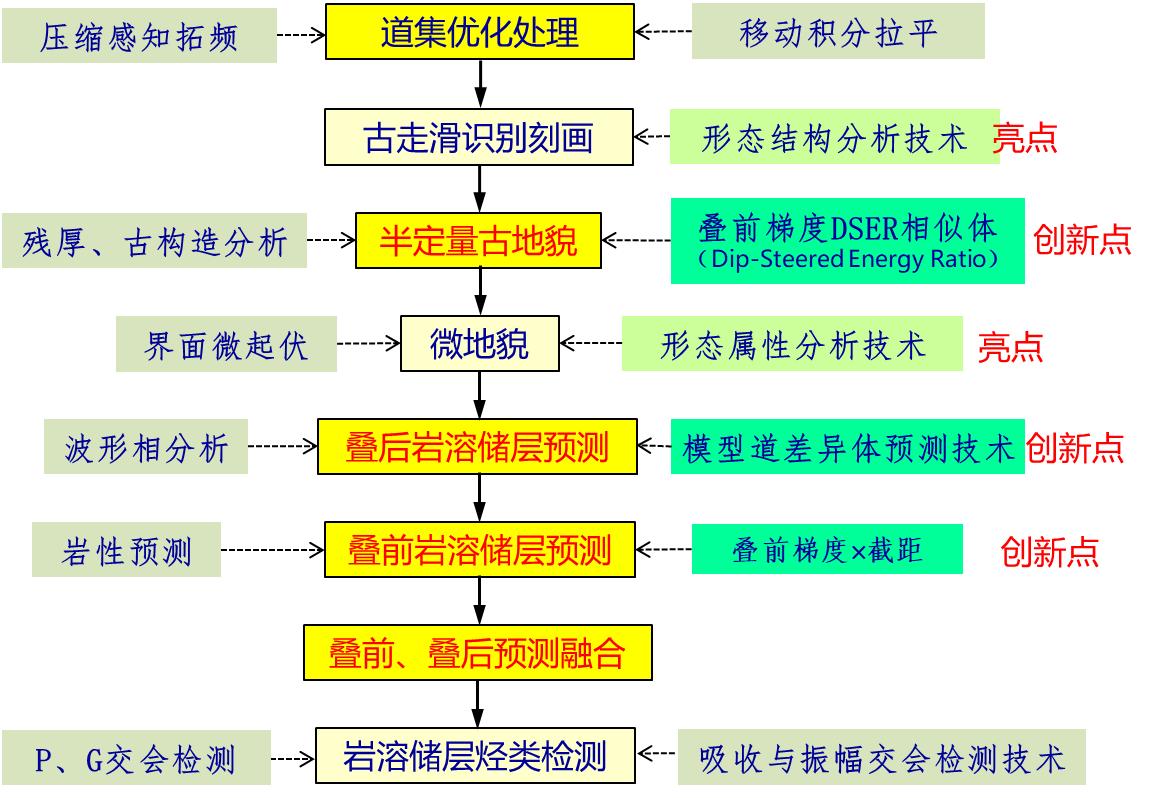
Figure 2-1 Key technical process of karst fracture-cavity reservoir prediction technology
Major Innovation results:
1、Paleogeomorphologic study combined with tectonic analysis, pre-stack and post-stack attributes
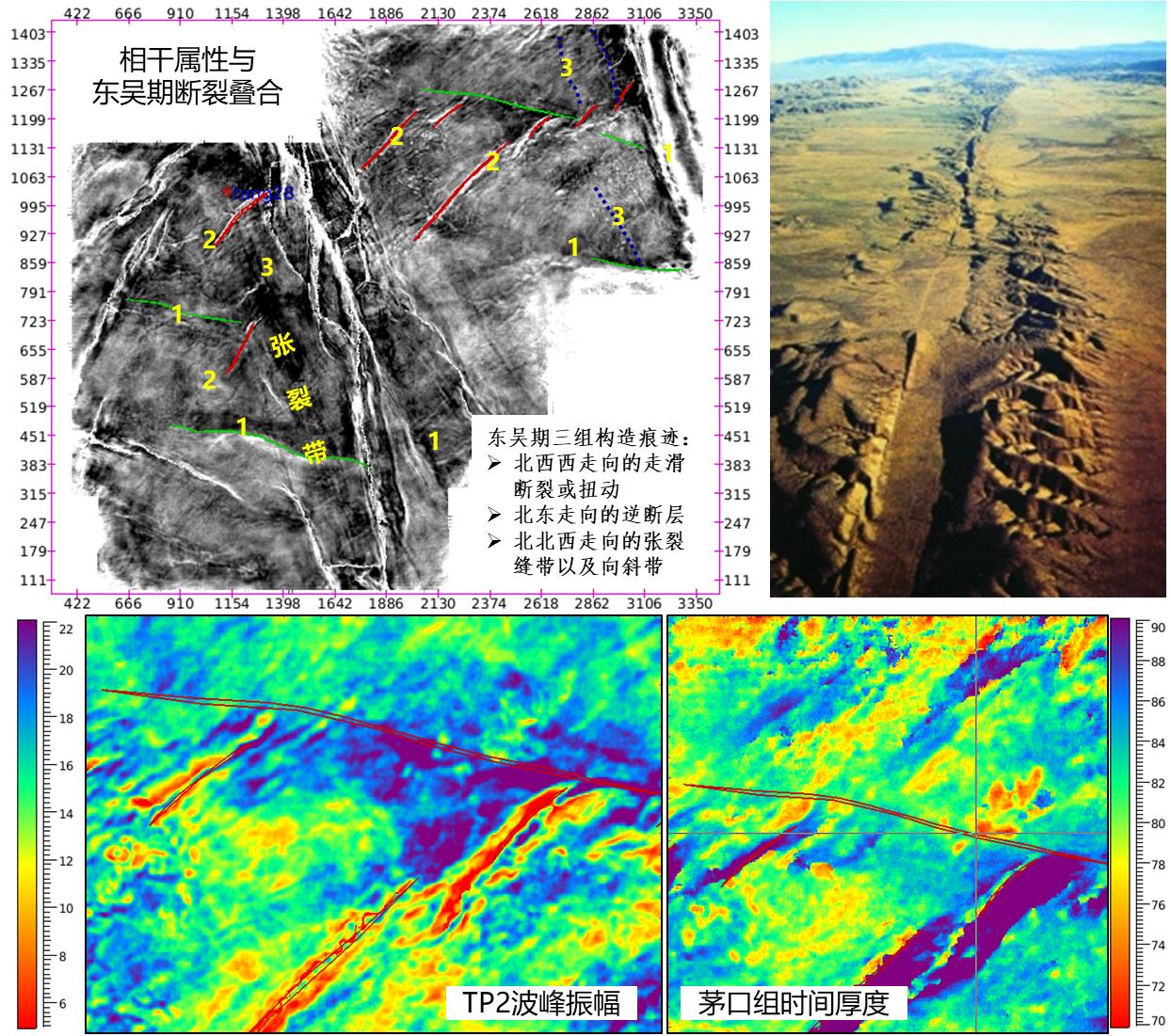
Based on the comprehensive analysis of seismic attribute, the development and distribution of ancient faults and tensile fracture zones, it is considered that the characteristics of ancient structures and faults are consistent with the structural characteristics under the dextral strike-slip stress system。Under the background of this dextral strike-slip torsional stress field, three groups of structural vestiges are developed: ①NWW-trending strike-slip faults, including identified and unidentified strike-slip faults or torsion; ②NE-trending reverse faults;③NNW-trending tension fracture and syncline zone. These tectonic phenomena controls or affects the ancient geomorphic morphology, the distribution of karst fissure and cave system. According to the analysis of maximum peak amplitude of TP2, the seismic amplitude is characterized by east-west zonation, which is far greater than the extension length of strike-slip fault.
The existence of strike-slip fault is obvious in geomorphology. The upper right is a typical strike-slip fault-controlled landform. The strike-slip fault-developed rift zone, lateral compressional uplift zone and other geomorphic features that match the strike-slip fault are clearly visible. In study area, the impact of strike-slip faults on landform is obvious. The strike-slip fault zone in the south of the work area, on flattened seismic section at bottom of Maokou Formation, has obvious geomorphic high zone, weak amplitude band in seismic attribute, and high amplitude band in east-west direction to the north. Obviously, the geomorphic height is closely related to the strike-slip fault.
On surface attribute of TP2 gradient similarity in Lizi 3D region, the regularity of gradient similarity is obvious, and there are four types of boundaries:
☆ Arc-shaped regular boundary: related to residual thickness, it is likely to be the boundary of lake basin in certain sedimentary period, and belongs to the smooth side bank after wave transformation. Saihai Lake of Meijiang River in Xitang, Guangxi is a karst lake with a very smooth shoreline.
☆ Small circle: pit or collapse
☆ The east-west straight boundary of internal full fold area: the boundary of similar body formed by strike-slip fault or torsion deformation.
☆ The boundary of nearly north-south and north-east directions is the boundary of similar bodies affected by faults.
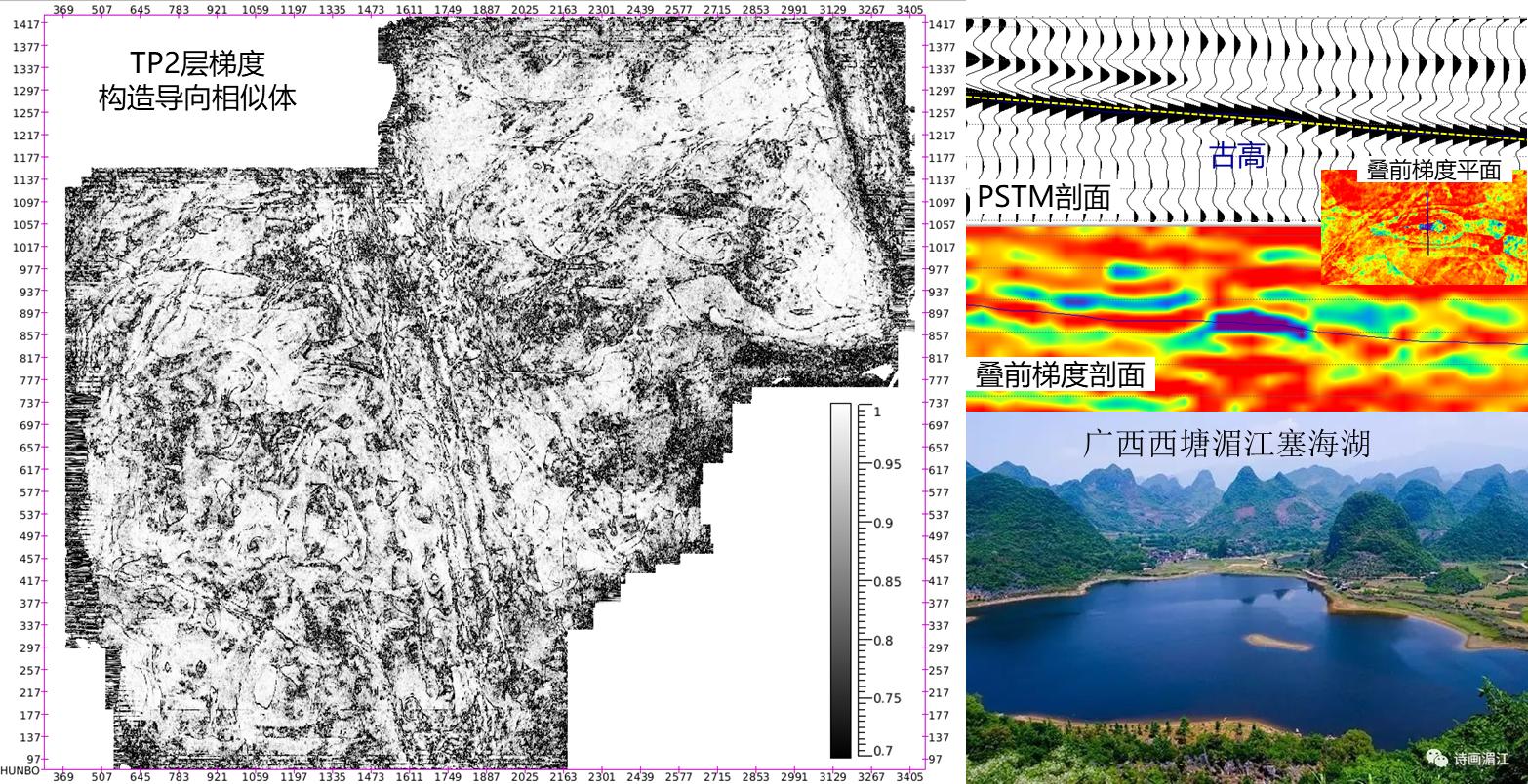
According to the arc smooth boundary, combined with residual thickness palaeogeomorphology and seismic attribute analysis, the relative elevation of the boundary of the similar body that may reflect the height of the palaeogeomorphology is interpreted. The change of pre-stack gradient attribute is complex, and it is related to multiple factors such as upper and lower strata, karst, oil and gas bearing property. Through the comprehensive analysis of gradient and gradient similarity attribute with landform and karst, the pre-stack attribute is closely related to ancient landform and karst. At the ancient high position, the post-stack seismic peak pinches out, pre-stack gradient attribute changes from negative to positive value, and lateral boundary is particularly smooth, like a knife cut.
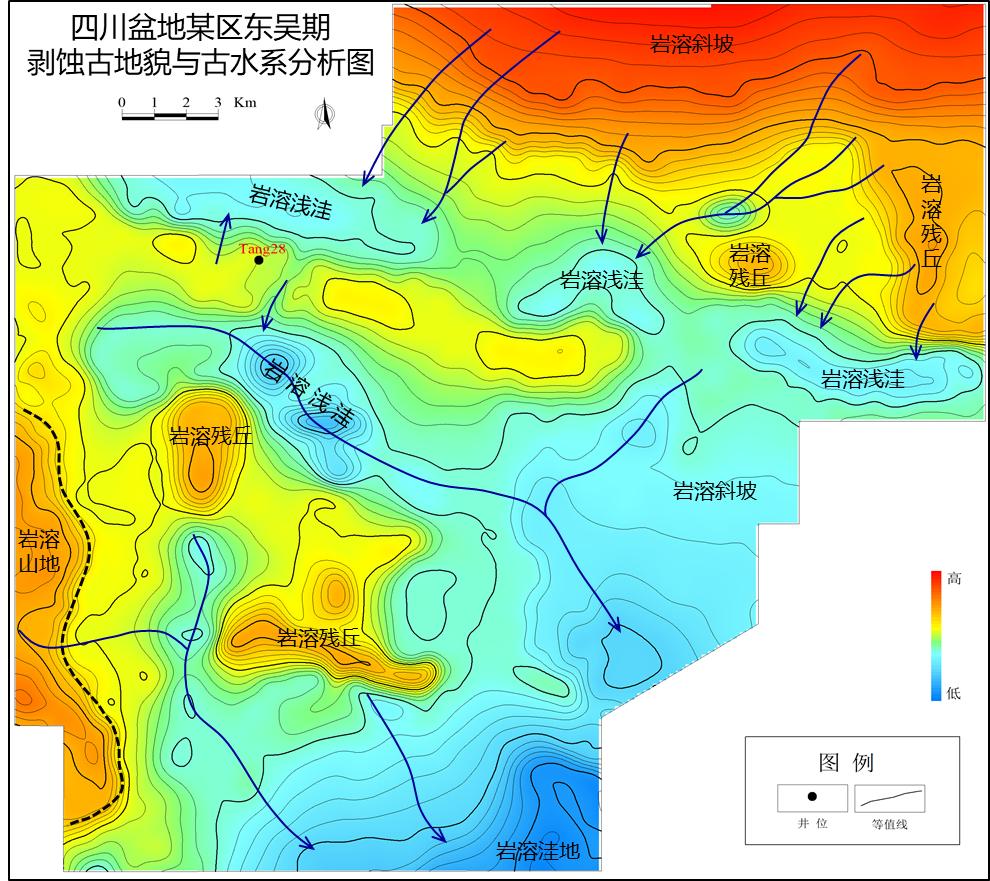
Based on the analysis of ancient surface elevation and microgeomorphology, combined with the analysis results of residual thickness method and impression method, the ancient geomorphology in this area is divided into: Karst mountain, karst residual hill, karst slope, karst shallow sag, karst depression and tension zone. The working area in the region is located on karst slope, with karst shallow sag developed locally, and karst depressions may develop locally in the south. Most areas are characterized by alternating of high and low zones. Under the background of above ancient landforms, the ancient water system in Lizi area is complex. The water system is affected by landforms such as high zones and residual hills. The water system has characteristics of multi-directional development and converging to southeast. Therefore, it is very possible to develop karst underground rivers from north to south by closing the south side of shallow sag zone.
2、Pre-stack and post-stack karst prediction
The project explores the model trace differential volume analysis technology, which analyzes the difference between each sample point and the model trace. It is sensitive to change, with high resolution, and is not constrained by the resolution of seismic data. Compared with curvature, coherence and other karst development analysis methods, it can conduct semi-quantitative karst development prediction, and also conduct waveform cluster analysis.
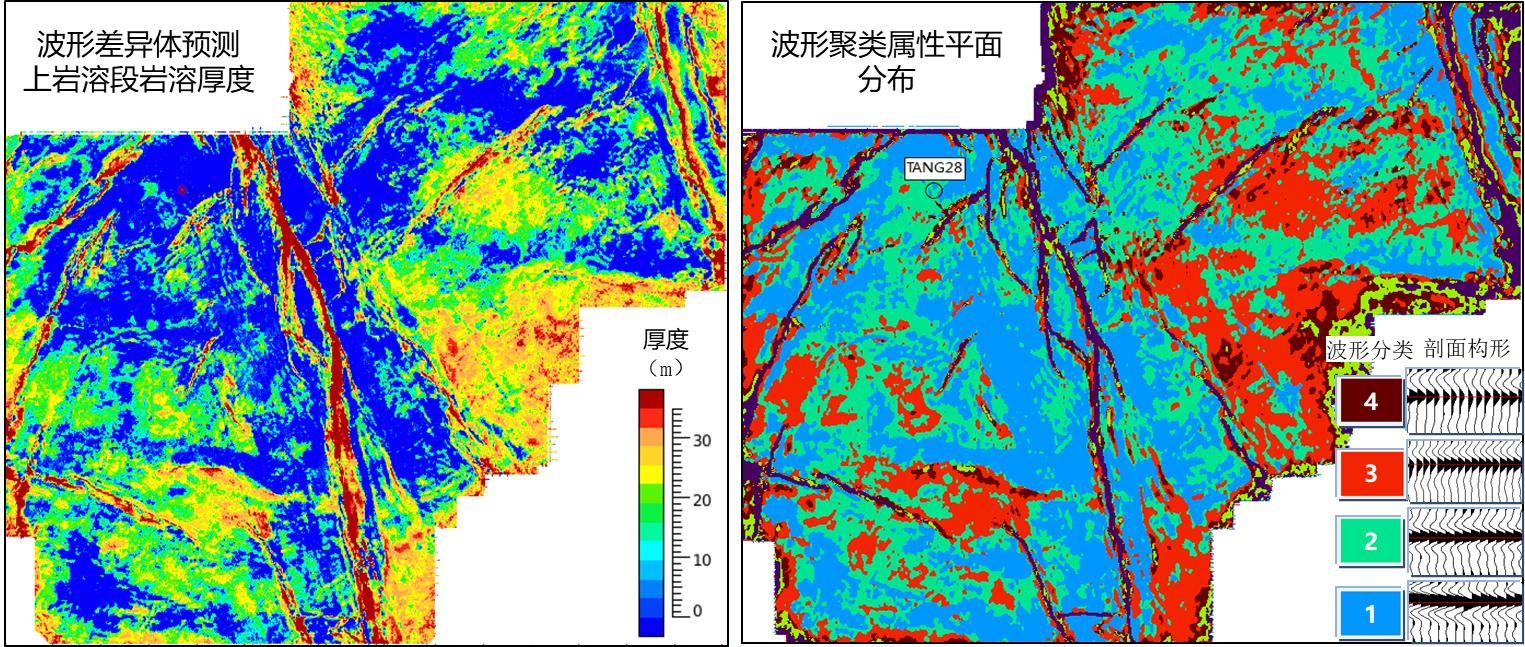
Pre-stack karst prediction: Pre-stack karst seismic prediction based on pre-stack gradient mainly detects the difference between the gradient characteristics of karst development section and the conventional carbonate seismic gradient characteristics, that is, the special characteristic attribute of positive P and positive G (P is positive and G e is positive in conventional formation). This conclusion is consistent with the development of karst residual hill in Tang28 well, and the high value zone is also a zone with large difference between seismic traces, which is consistent with the heterogeneity characteristics of karst development. The reliability of prediction results is not affected by the change of overlying strata, and is based on pre-stack attribute of gradient *intercept is the innovation of this project.